Excel users often have the need to split text in one column into one or more different columns. This tutorial provides step-by-step instructions for splitting textual data with Excel's Text to Columns feature.
Once the text in the cell looks like this, then we are ready to use the Text-to-Columns button to split the text up by the commas that separates each value. The key with using the SUBSTITUTE function is we want to replace each new line with a comma. The ASCII character code for a new line break is 10 for PCs and 13 for Macs. As we want to split the data in column A into two parts, Insert a column between columns A & B to place the second portion of the text. To insert another column, select column B and right-click on it, and then click insert, or we can use the shortcut key ( Ctrl with +).
Why split data? Often there is a need to sort, filter, or perform mathematical calculations on data that is not currently in its own column. A classic example is having first and last names in a worksheet column and wanting them in separate columns.
Rules for Successfully Splitting Excel Column Data
A. The data to be split must all have a common delimiter—one or more characters that create a boundary. Delimiters can be spaces, commas, tabs, or any symbol or special character not found in the data itself.
B. Excel puts the split data in one or more columns to the right, so insert several empty columns before doing a split so Excel won't overwrite existing data.
C. Some cells may not split correctly. For example, if splitting names with a space as the delimiter, entries with a middle name, like Sue Ann Jones, will split into three columns instead of two, and will have to be corrected. See the last section for more information.
How to Split When Comma, Semicolon, Tab, or Space is the Delimiter
Follow these directions if the delimiter is a comma, tab, space, or semi-colon.

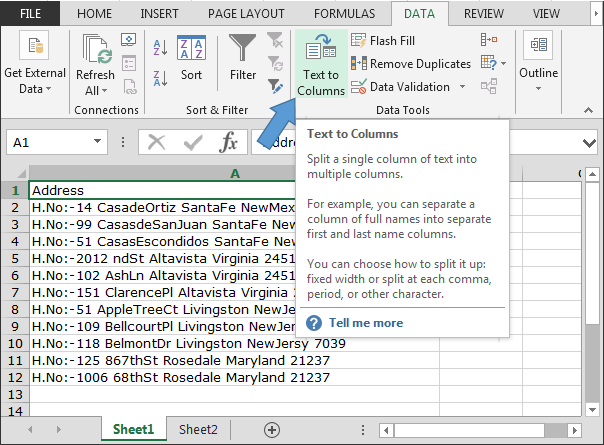
► 1. Make sure you have one or more empty columns to the right. Then select the cell whose contents you want to split. In our example we select Column A.
► 2. On the ribbon's Data tab, find the Data Tools section and click Text to Columns.
► 3. The Convert Text to Columns wizard opens. Select Delimited and click Next.
Split Text To Columns In Mac For Addresses Online
► 4. Now we specify which character Excel should use to split the data. Make sure a checkmark is in just one of the boxes under Delimiter—Comma in our example. A preview of the results displays at the bottom. Click Next.
► 5. The last window lets the user select each column's data format. If you don't want to use the default, highlight each column and make a selection. Then click Finish.
► 6. Excel returns to the worksheet with the first column highlighted. The split data in the new column will have the worksheet's default color and font.
How to Split When a Symbol or Special Character is the Delimiter
Data may also be separated by hyphens, dashes, slashes, pipes, or any symbol or unique character. If so, follow these steps. (And see the last section for potential problems if the character used as the delimiter is also in the data itself.)
► 1. Insert one or more empty columns to the right. Then select the cell whose contents you want to split. In our example, a hyphen is the delimiter.
► 2. On the ribbon's Data tab, find the Data Tools section and click Text to Columns.
► 3. The Convert Text to Columns wizard opens. Select Delimited and click Next.
► 4. Under Delimiters, ensure only Other is checked, and type the character you're using as the delimiter in the white box. A preview at the bottom shows the data when split. Click Next.
► 5. Modify the data format for each column if desired, or take Excel's default format. Then click Finish.
► 6. Excel returns to the worksheet with the data split into two columns and the first column highlighted.
Problem: Inaccurate Splitting of Data
Split Text To Columns In Mac For Addresses
If the delimiter appears elsewhere in the data, some results will be inaccurate. In this example, both a book title (Dog-Friendly Hotels) and an author's last name (Ron Smith-Davies) contain hyphens—our delimiter. Because Excel will split the data every time it sees a hyphen, rows 2 and 3 have extra columns as seen in the preview image below.
So add extra blank columns to the right before splitting the data, look at the preview, and correct any errors after the split.
Over-writing Existing Worksheet Data
When using Text to Columns, Excel uses as many columns as necessary to complete the split. In this example, the delimiter, a space, is repeated in the data, and we've only one blank column. So a column of data will be overwritten.
When Excel needs to overwrite existing data to complete a split, it displays this warning.

If we click OK, Excel completely overwrites the next column (or columns) regardless of how many rows actually need the extra cell. In our sample worksheet, Column F contained the Hire Dates, but now all of that data is gone!

Being able to split cell data into multiple cells is a great Excel feature. But inspect your data carefully, leave extra blank lines for potential issues, look at the preview before finishing, and correct any problems after splitting the data. We hope this article on splitting data from one column into multiple columns has been helpful. Cheers!
↑ Return to the top
Very often you may have to manipulate a column of text in a data frame with R. You may want to separate a column in to multiple columns in a data frame or you may want to split a column of text and keep only a part of it.
tidyr’s separate function is the best option to separate a column or split a column of text the way you want. Let us see some simple examples of using tidyr’s separate function.
Let us first load the R packages needed to see the examples with separate function.
Let us create a small data frame with a column of text separated by underscore.
The data frame contains just single column of file names.
How to Split a Single Column into Multiple Columns with tidyr’ separate()?
Let us use separate function from tidyr to split the “file_name” column into multiple columns with specific column name. Here, we will specify the column names in a vector.
By default, separate uses regular expression that matches any sequence of non-alphanumeric values as delimiter to split.
In this example, tidyr automatically found that the delimiters are underscore and dot and separted the single column to four columns with the names specified.
Often you want only part of text in a column. Let us see another example of a data frame with column containing text, but this time we specify only three columns for our output.
Split Text To Columns In Mac For Addresses Without
Note that we provide just three columns in separate function.
The output of separate() in this example contains only three column as we specified. And we also see a warning, since we left out the extra element present after separating the text.
We can use argument extra=’drop’ to specify separate to drop anything extra without warning us.
Similarly, if we want only the first element after splitting, we can just specify only one column for our output.
If you want an element that is in the middle after separating with separate, we can use dplyr’s select function select the column needed. For example, if we need the second element ‘Month’, we can combine tidyr’s separate with dplyr’s select.
unite() to combine multiple columns to a single column
Sometimes you may want to do opposite ehat separate can do, i.e. combine multiple columns into a single column. You guessed it right, tidyr has a cool function to do that. tidyr’s unite() complements separate() and combine multiple columns into a single column.
Let us see an example of unite() combining two columns created by separate(). Here, we first separate a column into three columns and then use unite() to combine the first two columns into a single column.
The output is a dataframe with two columns, where the first column is the result of unite().